Understanding the Effects of Minimum Wage Increases on Chicago’s Local Businesses
How Rising Minimum Wages Influence Chicago’s Small and Medium Enterprises
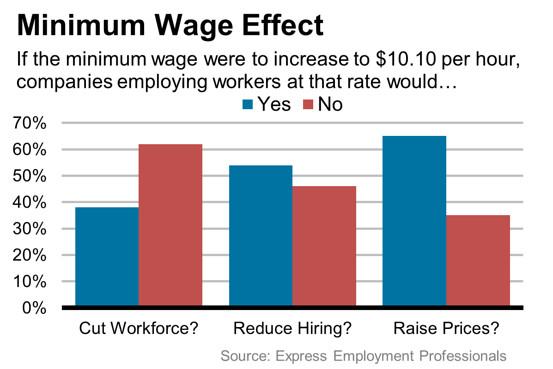
As Chicago enacts higher minimum wage laws, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) find themselves navigating a complex economic habitat. While the wage hikes are designed to improve workers’ quality of life, many businesses must swiftly adapt their financial models. This often involves revising pricing, adjusting staffing levels, or modifying work hours to stay afloat. Industries like retail and hospitality have especially felt the squeeze, with profit margins tightening and operational costs rising.
Nevertheless, some businesses view these changes as a catalyst for positive change. By investing in employee development and retention strategies, they aim to counterbalance increased payroll expenses with enhanced productivity and customer service. The table below summarizes the main economic impacts experienced by Chicago SMEs following the wage increase:
| Aspect | Benefits | Obstacles |
|---|---|---|
| Workforce Dynamics |
|
|
| Operational Adjustments |
|
|
Innovative Approaches to Managing Elevated Labor Expenses
To counterbalance the financial impact of wage increases, many Chicago businesses are revamping their operational strategies. Automation tools, such as smart scheduling software and streamlined payroll systems, are becoming essential for optimizing labor deployment. These technologies help minimize overtime costs and ensure adequate staffing during peak periods. Additionally, some companies are shifting towards merit-based pay structures to maintain employee motivation without uniformly increasing wages.
Cost containment efforts also extend beyond labor, with firms scrutinizing procurement processes and trimming non-labor overheads. Cross-training employees has emerged as a popular tactic, especially in service industries, to enhance workforce versatility and reduce reliance on temporary hires. Key strategic adjustments include:
- Utilizing part-time and seasonal staff to align labor supply with demand fluctuations.
- Implementing retention programs to lower turnover-related expenses.
- Leveraging advanced analytics for precise labor forecasting.
| Strategy | Anticipated Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automated Scheduling | Reduction in labor costs by 10-15% |
| Employee Cross-Training | Greater operational flexibility |
| Performance-Based Incentives | Enhanced employee engagement |
Maintaining a Balance Between Workforce Well-being and Business Viability
Raising the minimum wage places employers at a pivotal crossroads. While improved compensation directly benefits employees, businesses-especially SMEs-must reconcile these costs with the need to remain competitive. Many are responding by streamlining workflows, adopting automation, and redesigning shift patterns to safeguard profitability without undermining employee satisfaction.
Achieving equilibrium often involves targeted initiatives that support both staff welfare and operational sustainability. Examples of such measures include:
- Boosting productivity through specialized training programs
- Negotiating better terms with suppliers to reduce input costs
- Introducing flexible work schedules to lower overhead
- Employing technology to offset labor-related expenses
| Approach | Effect | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | Minimizes repetitive manual tasks | Self-service checkout stations |
| Flexible Scheduling | Optimizes employee coverage | Rotating shift patterns |
| Supplier Negotiations | Reduces procurement costs | Bulk purchase agreements |
Policy Suggestions to Aid Businesses Amid Wage Increases
To ease the burden of rising labor costs, policymakers should consider implementing supportive measures tailored to the needs of local businesses. Initiatives such as tax incentives for SMEs, subsidized workforce training, and grants for adopting labor-saving technologies can provide critical relief. These programs not only alleviate immediate financial pressures but also promote innovation and long-term economic resilience.
Moreover,fostering collaboration between government bodies and the private sector can create a dynamic environment that adapts to evolving economic realities. Recommended policy actions include:
- Phased wage increase schedules to allow businesses time to adjust
- Expanded access to affordable healthcare to manage indirect labor costs
- Support for vocational and skills training to enhance workforce capabilities
- Data-driven policy evaluation to monitor impacts and refine strategies
| Policy Initiative | Objective | Projected Result |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Incentives | Lower payroll expenses for small businesses | Increased employment opportunities |
| Training Grants | Enhance employee skills and efficiency | Higher productivity levels |
| Technology Funding | Encourage automation adoption | Reduced operational costs |
Looking Ahead: Navigating the Future of Labor Costs in Chicago
The ongoing discussion surrounding minimum wage increases demands a nuanced understanding from both business leaders and policymakers. While the goal remains to improve workers’ earnings and quality of life, the accompanying challenges for employers necessitate thoughtful strategies. The multifaceted effects on staffing, pricing, and operational models underscore the importance of continuous evaluation and adaptive solutions. By balancing employee welfare with sustainable business practices, Chicago can foster a resilient economy that benefits all stakeholders.