Analyzing Crime in Chicago: Current Patterns, Causes, and Solutions
Shifting Crime Patterns Transforming Chicago’s Urban Environment
Chicago continues to grapple with a multifaceted crime landscape that evolves alongside its diverse neighborhoods. While violent offenses remain a critical issue, recent data reveals a surge in property crimes, cyber offenses, and gang-related incidents, each reshaping the city’s public safety challenges. These developments demand innovative responses that blend technology, community involvement, and adaptive policing methods to effectively mitigate crime.
Key emerging crime dynamics include:
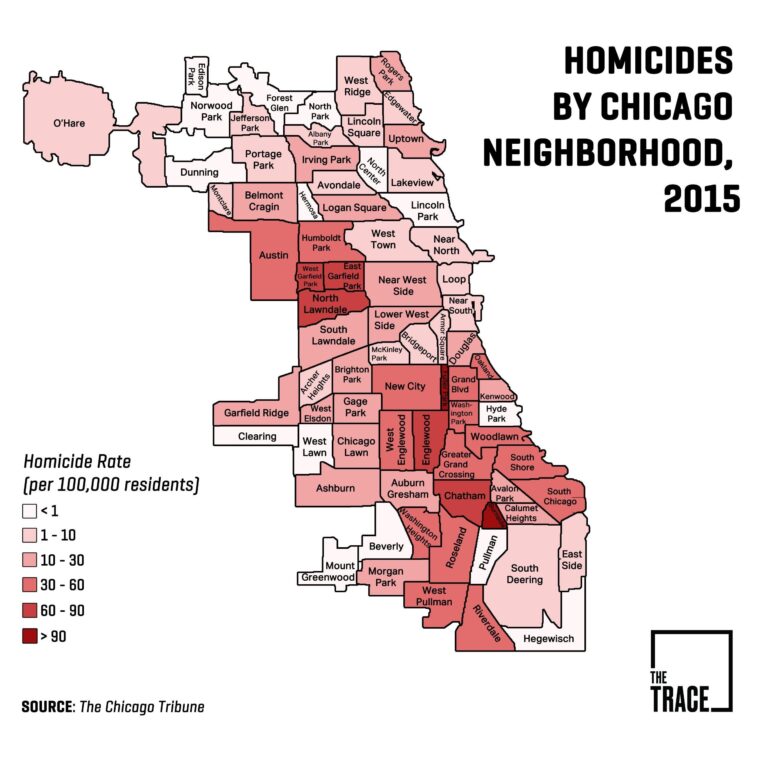
- Neighborhood Variability: Persistent violent crime hotspots remain concentrated in parts of the South and West Sides, whereas northern districts report rising incidents of theft and identity fraud.
- Demographic Influences: A growing population of digitally literate youth both contributes to cybercrime risks and fuels progressive community policing initiatives.
- Economic Strain: Increasing unemployment and housing instability correlate with higher rates of non-violent offenses that nonetheless impact community wellbeing.
| Crime Category | Incidence Rate per 100,000 (2023) | Annual Change |
|---|---|---|
| Violent Crime | 620 | +5% |
| Property Crime | 1,450 | +12% |
| Cybercrime | 300 | +25% |
| Gang-Related Crime | 450 | +7% |
Unpacking the Underlying Drivers of Chicago’s Enduring Violence
The persistent violence in Chicago is deeply rooted in a web of social and economic disparities. Chronic poverty limits access to essential resources, fostering environments where crime can flourish. High unemployment, coupled with insufficient educational and housing opportunities, creates fertile ground for violent behavior. Moreover, entrenched gang networks intensify territorial conflicts, often escalating into violence that affects entire communities.
Primary factors fueling violence include:
- Widening economic inequality and restricted social mobility
- Historical segregation and chronic underinvestment in marginalized neighborhoods
- Inadequate mental health and social support infrastructure
- Easy access to illegal firearms
- Deep-seated mistrust between residents and police forces
| Factor | Effect on Crime |
|---|---|
| Economic Hardship | Reduces lawful opportunities, heightens susceptibility to crime |
| Community Neglect | Weakens social bonds and erodes trust in institutions |
| Illegal Firearm Circulation | Amplifies violence severity and fatality rates |
| Challenges in Policing | Diminishes cooperation and accurate crime reporting |
Collaborative Initiatives Between Communities and Law Enforcement
Efforts to curb crime in Chicago increasingly rely on partnerships between residents and police departments. Community-driven programs such as neighborhood watch groups have revitalized local vigilance, serving as vital deterrents to criminal activity. These grassroots movements are bolstered by law enforcement’s shift toward community policing, which emphasizes trust-building and open dialogue over customary enforcement. This approach has led to improved dialogue, greater public confidence, and more effective crime prevention.
Notable strategies enhancing public safety include:
- Youth Outreach Programs: Collaborative mentorship and educational initiatives designed to divert young people from criminal pathways.
- Technological Tools: Deployment of crime-mapping software and expanded surveillance in high-risk areas to enable rapid response.
- Community Forums: Regular meetings that foster obvious conversations between citizens and law enforcement about safety concerns and solutions.
| Program | Participants | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Neighborhood Watch | Local Residents | 15% reduction in minor crimes |
| Community Policing | Chicago Police & Community Members | 10% decrease in violent crime, improved trust |
| Youth Mentorship | Schools and Nonprofits | Increased school retention, fewer gang involvements |
Strategic Policy Directions for Long-Term Crime Mitigation
Combating crime in Chicago demands a thorough approach that centers on community empowerment and strategic resource deployment. Investing in grassroots programs that engage local leaders and youth is critical to interrupting cycles of violence early. Expanding access to mental health care, vocational training, and education creates viable alternatives to criminal activity. Transparent and accountable policing further strengthens community relations, fostering safer neighborhoods over time.
Policies grounded in data analytics and continuous evaluation optimize the allocation of law enforcement resources and program funding. The table below contrasts conventional crime control methods with lasting, community-focused strategies:
| Conventional Approaches | Progressive Strategies |
|---|---|
| Heavy dependence on incarceration | Focus on rehabilitation and reintegration programs |
| Reactive enforcement tactics | Proactive community engagement and crime prevention |
| Minimal interagency cooperation | Coordinated efforts across social services and law enforcement |
| Short-term crime rate focus | Emphasis on long-term safety and social equity |
- Strengthen community policing: Foster trust through consistent, respectful interactions.
- Expand social support systems: Tackle root causes like unemployment and trauma.
- Utilize advanced technology: Apply predictive analytics for efficient resource deployment.
- Maintain transparency: Ensure public accountability through regular reporting.
Final Thoughts
Understanding Chicago’s crime challenges requires a detailed examination of evolving trends, foundational causes, and collaborative interventions. Even though obstacles persist, ongoing prevention and reform initiatives provide hope for safer communities. Staying informed through authoritative sources such as the Council on Criminal Justice empowers residents,policymakers,and stakeholders to contribute meaningfully to the city’s pursuit of justice and security.